You might think that once you’ve got your Wi-Fi network all set up and running, then that’s it done. But it’s not! Having a reliable wireless network involves ongoing maintenance and health checks to make sure that it’s performing at its optimum level.
There are plenty of variables in a wireless network that could change. Things like user demand or changes in the radio frequency that could have an impact. Seemingly simple things like rearranging your office furniture, onboarding new employees or using more applications requiring bigger bandwidth can all be negative factors affecting your Wi-Fi network.
Ongoing, regular surveys can help you catch these changes before they start to cause you too many problems.
So what do you need to do to keep your wireless networking functioning effectively?
Monitor New Client Devices
Just as when you are in the design and planning stages, it’s vital to know the number of users that are connected at any one time, and what devices they are connecting to the network with. Your network performance depends on this!
This could likely change with company growth or if your business has seasonal staff where connections peak and trough.
It’s also worth bearing in mind how old the devices are. Older laptops, for example, won’t work so well with today’s modern networks. And vice versa!
You can counteract this by semi-regularly updating your devices to align with your network.
Likewise, if your network was originally deployed a while ago, without being monitored or updated it will fail to work with modern devices to their potential.
You need to also monitor the applications being used and ensure that the bandwidth matches the demand. Organisations like schools that now have a plethora of laptops connecting wirelessly to the school network need to have strong, reliable Wi-Fi. Hospitals also have high bandwidth demand with the ‘workstations on wheels’ that are now prevalent.
The more end users you add to your network, the more bandwidth you will need.
In simple terms – Make sure you are monitoring new client devices. Make it your business to keep track of how many devices are connecting to your network and make sure you can meet the Wi-Fi demand consistently. Your business operations depend on it.
App Usage and Progression
As we all know, technology is constantly evolving. Device manufacturers are always striving for the fastest, most powerful offering to stay ahead of their competitors.
This means that apps and software also move fast to keep up. This constant evolution means that you need more and more data with every update. Thus, the requirements of your Wi-Fi network are likely to change and be modified accordingly.
Wireless is often the first choice – If not the only choice! So you need to make sure your business Wi-Fi offering is up to scratch.
Physical Changes in the Office Landscape
You might not think too much about rearranging the office, but this could have a significant impact on your coverage area and how your access points function.
Tweaks like going from open plan to individual offices (or the other way around) will change the way your AP’s perform in your office space.
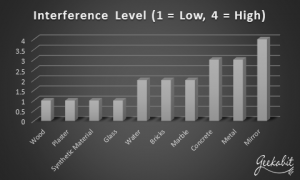
Interior walls (or lack of them) will affect the radio frequency and how it attenuates. You might be thinking, surely removing partition walls to make an open plan office couldn’t cause Wi-Fi problems. Ut actually it could! The RF will be able to travel further without any attenuating interior walls, meaning it could start contending with other channels and cause interference.
Any physical changes in your office environment need to be surveyed to see if and how it will affect how your Wi-Fi network functions. This means you can make the necessary adjustments before problems arise.
Identify Common Causes of RF Interference
Following on from physical changes in your office environment, you need to also be aware of other possible causes of RF interference.
Once possible source of interference on your Wi-Fi network could be noise from neighbouring networks. Other AP’s in range of your coverage area could cause RF interference, especially if their power levels are turned up.
Wi-Fi interference is when you have AP’s that are operating on the same or adjacent frequencies. This can cause interference or contention on these channels, or Overlapping Basic Service Set (OBSS). If your network is experiencing this type of interference, you could see your ability to send or receive data significantly reduce or even completely disabled.
You can also get non–Wi-Fi Interference from devices that use other radio networks. Things like microwaves, monitors, blue tooth or surveillance cameras could all cause interference problems.
Your Business Depends on your Wi-Fi Network
If you’ve gone to the effort of designing and planning the optimum network for your business, then don’t waste that work by not monitoring and maintaining it.
Even the best networks will need tweaks and changes over time, to make sure it can keep up with the demands of new users and modern devices.
Regular monitoring or ‘Wi-Fi health checks’ can help identify problems while they’re still small – Allowing you to get them sorted out before they start causing your business serious issues. Don’t wait until the IT department are inundated with calls from frustrated, unproductive employees.
If you think your wireless network is in need of a health check, why not give us a call here at Geekabit? Our wireless experts have the knowledge and expertise to diagnose and solve your Wi-Fi problems, improving the reliability and functionality of your business Wi-Fi.