A recent study seems to think so. Current research with foundations in monitoring and examining mobile phone reception, appears to show that despite your handset indicating a 5G signal, it actually only has a 4G connection.
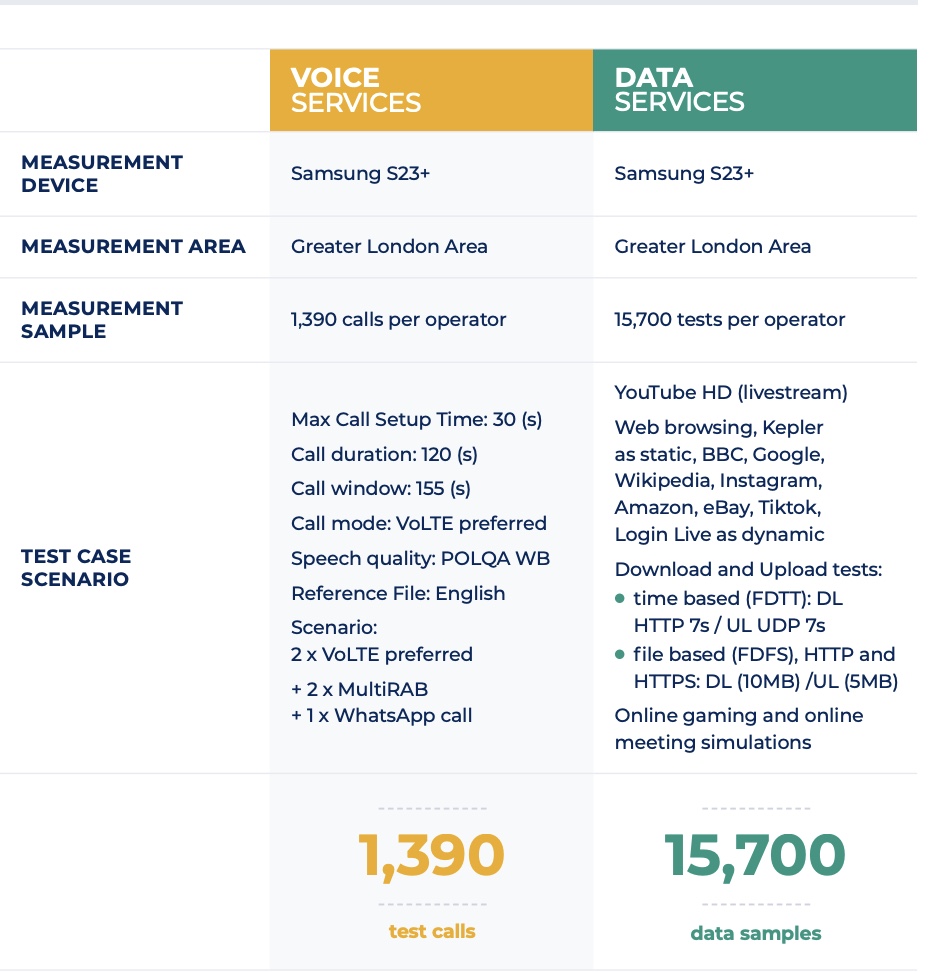
Samples taken from UK testing showed 38% of connections were 4G, even though the 5G icon was being shown. 11,000 tests were carried out over a period of 2 months at the start of this year.
Why would a handset indicate it’s connected to 5G, if it’s actually using a 4G connection?
It can differ from phone to phone, but for many if the phone is connected to a base station that has 5G equipment potentially available, then it will show the 5G icon. However, in real usage terms the connection may be using 4G or 5G.
Some phones will change the distinction of the icon depending on whether an actual 5G connection is made. Others will show the same 5G icon whether the 5G connection is only available or actually connected.
The above image shows an area map of Central London where testing was carried out. The red shows actual 5G connections, and the blue indicates where a 5G icon is displayed but a 4G connection is made.
As you can see for yourself, a 4G connection being used under the guise of a 5G connection is a common one.
This issue isn’t anything new, but what is new is the research looking at how this is impacting our connections in the UK.
With an average speed of 49 Mbps, this recent study found when testing that mobile broadband via actual 5G is approximately twice as fast as where it’s a 5G icon only (27 Mbps).
Is 4G masquerading as 5G happening across all UK mobile networks?
The results from this study were taken from a sample across all the UK mobile networks. However, it did find that it was more common with some operators than others to display the 5G icon despite being connected to 4G.
Let’s have a little look at each mobile network. According to study tests, when the 5G icon is displayed, what percentage of the time are you actually getting a genuine 5G connection?
Three UK: 94% of the time
Vodafone: 93%
O2: 66%
EE: 32%
These findings are surprising, as other surveys and studies have found EE to do well in 5G performance in terms of data and coverage.
It’s important to bear in mind that getting a 5G connection everywhere is likely not possible, and people would largely accept a 4G connection in its place where 5G isn’t a possibility. The important bit, perhaps, is the visibility to consumers in terms of what they are actually getting moment to moment. Customers should know whether they are connected 4G or 5G and not just shown a blanket 5G icon where there is merely potential.
We’re all for using 4G in places where that connection is going to be stronger and more reliable than a 5G connection. But let’s make sure customers are aware when this is happening.