Have you ever arrived at a conference, sporting event or hotel only to be greeted by a frustratingly slow internet connection? Whether you are trying to access work emails, share a clip of an amazing goal or just laze in your room binge watching your favourite show on your smartphone, we’ve all felt that frustration at a sinfully slow connection.
If only you could check a venue’s connection quality before you book…
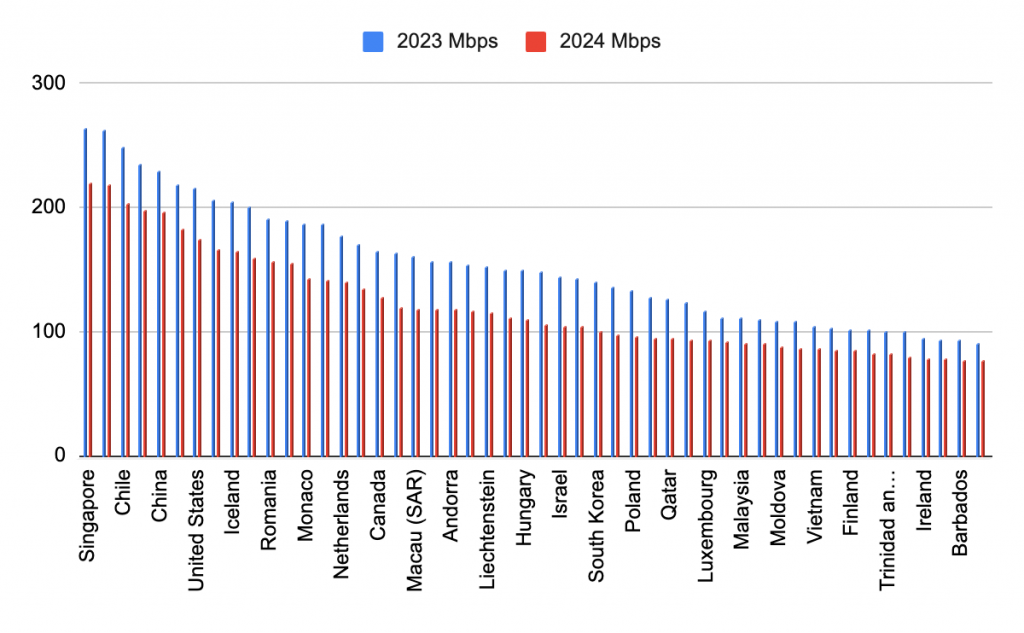
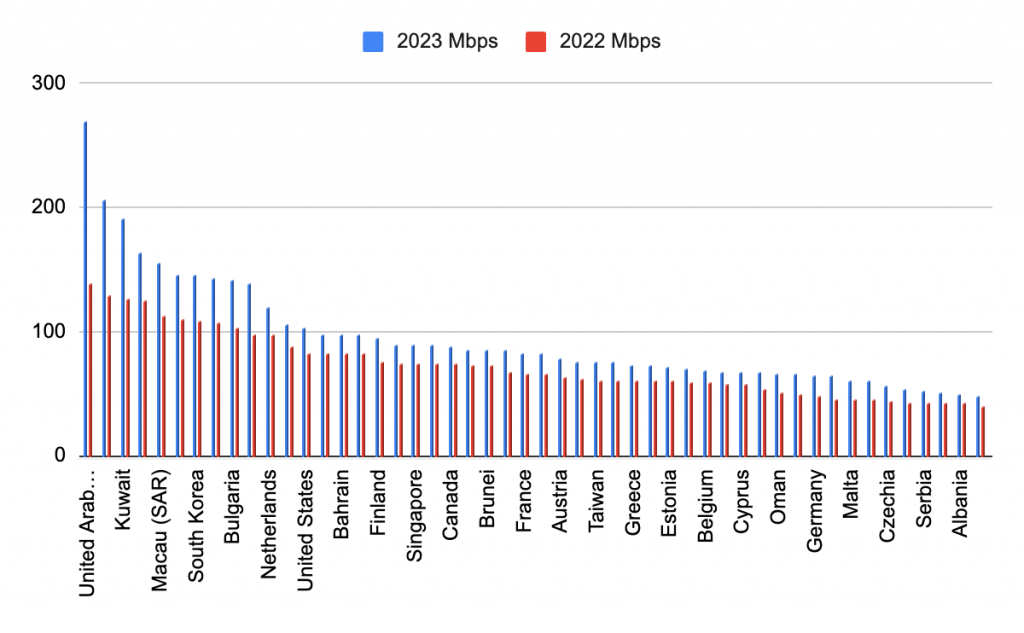
Ookla, a network testing business which collects consumer data through their popular broadband testing service Speedtest.net, launched a new Speedtest Certified™ scheme last week.
The thinking behind this new scheme is to be able to offer people and businesses verification on ‘superior connectivity.’ Think places like hotels, stadiums, event venues, office buildings, and airports.
As a consumer, you want to know these venues are going to be able to offer an excellent connection while you are visiting. As a business, you want to be able to offer verification of that excellent connection before they’ve even arrived.
How Can You Prove to Customers that Your Business Offers Superior Connectivity?
As a business owner, you may be one of the many properties identified by Ookla who are keen to prove their connectivity to their potential customers, demonstrating their readiness to meet everyone’s connectivity expectations and needs.
This new service from Ookla, Speedtest Certified™, is designed to give businesses the proof they need.
The newly launched program aims to provide a “trusted badge of excellence“ to venues like hotels, stadiums, airports, event venues and office buildings. Based on Ookla’s globally recognised reputation for mobile and broadband performance measurements, this verification of excellent broadband and connectivity will help businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors and show how committed they are to aiding their customers’ digital experiences.
How Will Speedtest Certified™ from Ookla Deliver This Verification Scheme?
The entire approach will be data-driven, enabling the provision of comprehensive and objective assessment of a venues network. The following key variables will be measured:
- The quality of Wi-Fi radio frequency (RF)
- Wi-Fi network configuration
- Wi-Fi network security assessment
- Network performance metrics
- ISP backhaul
If you’ve trusted Ookla’s popular Speedtest platform to manage your own connectivity, then you’ll likely be excited at the prospect of knowing just how good the internet connection will be, BEFORE you arrive at an event or hotel. In the words of Stephen Bye (President and CEO of Ookla, Ziff Davis Division) the new Speedtest Certified™ scheme will give you ‘a seal of approval you can count on’ when it comes to reliable connectivity.
5 Star Rating for Internet Speed
Properties that meet or exceed the rigorous standards of Ookla’s Speedtest Certified™ will earn themselves a high-value certification backed by the trusted Speedtest name. This trusted Badge of Excellence will give them a star rating out of 5 for speed and will be valid for 1 year, after which the venue must be re-certified to ensure they still meet the necessary connectivity standards to keep that status.
Not only will they be able to share their Speedtest badge of honour for superior connectivity, businesses will also have access to Ookla’s Speedtest Certified Digital Platform. Here they will be able to:
- Access personal insights
- Benchmark performance against other Speedtest Certified Networks
- Receive targeted recommendations for improvements
Can We Expect the Same for Mobile Connectivity?
The initial Phase One launch is aimed at Wi-Fi connectivity and performance inside properties such as the ones mentioned above.
Phase Two of this programme will look at assessing cellular performance testing in terms of 4G/5G mobile. It’s likely we’ll see this rolled out in the coming months.
What if Your Business Wi-Fi Isn’t Up To Standard?
This new Speedtest Certified™ scheme launched by Ookla is great – If your business or event venue has the superior connectivity that the standards insist upon.
What if your internet speed star rating falls short and your venue’s connectivity doesn’t meet the required standards?
There is always something that can be done to improve your Wi-Fi network and connectivity for customers.
If your business struggles with slow Wi-Fi, an unreliable connection or any other Wi-Fi issues, then our Wi-Fi Experts here at Geekabit can help.
Whilst you’re probably tearing your hair out with frustration, we actually love Wi-Fi problems like slow speeds, Wi-Fi dead spots or users unable to connect – Because we know what a huge difference we will be able to make to you and your business.
Using globally renowned specialist measuring and testing equipment, we can get to the root of the problem. Though Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Planning & Design and Wi-Fi Installation we can get your business’ connectivity working just as it should be.
We’ve helped hotels, warehouses, corporate offices and stadiums to name just a few. We can also help with event Wi-Fi!
So don’t put up with dodgy Wi-Fi any longer – It’s time to call in the experts. Contact Geekabit today.
Imagery used with thanks from https://www.ookla.com/speedtest-certified