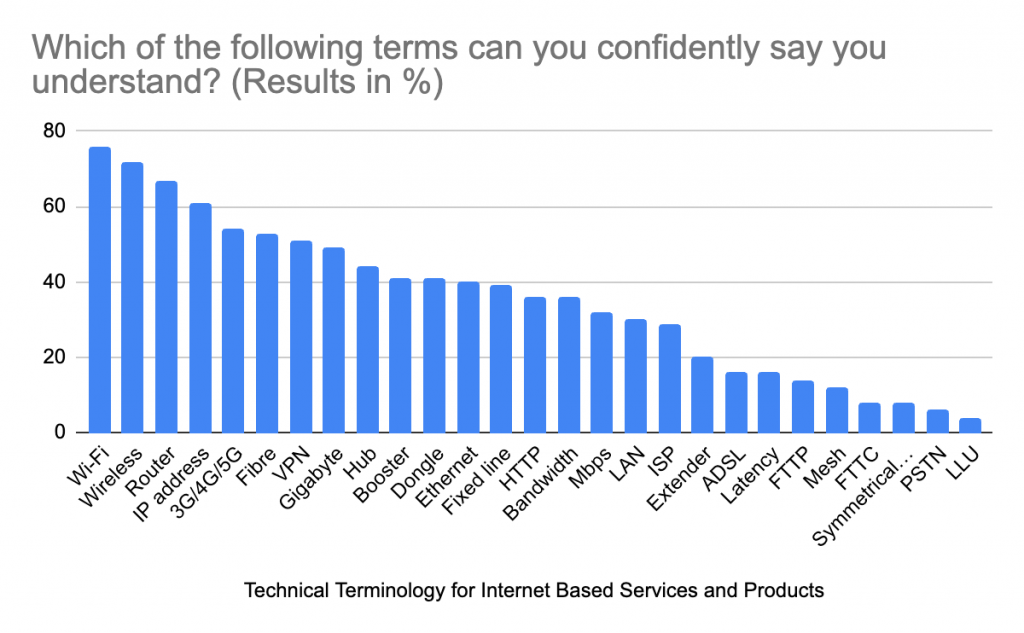
Like with so many of our utilities, we only really notice them when there’s a problem or they’re not working properly. Wi-Fi is just the same! Just like when the power goes out, if your Wi-Fi is on the blink then you know about it – And it is so frustrating!
Whilst most people are lucky enough to connect to superfast broadband through a wired connection, there are also many rural homes that cannot access and connect to broadband or internet in the same straightforward way.
Here at Geekabit, we work with lots of people – Businesses and homes – who struggle with the more traditional ways of connecting to the internet and have to turn to mobile broadband through 3G, 4G and 5G.
And again, many people are lucky to have a business or home within range of a strong enough UK mobile broadband network.
‘Could I benefit from an external antenna?’
There are some more remote rural homes and businesses that find themselves struggling to connect to mobile broadband too. If your business or home is:
– Unable to connect to a decent fixed line ISP
– Within range of a mobile broadband alternative but find it unstable on various operators
Then you might find it beneficial to get an external antenna installed. But which one do you need?
Are External Mobile Broadband Antennas Easy to Install?
In terms of actually installing an external antenna, it’s actually pretty straightforward. All you need to do is choose a high, stable location on the outside wall of your house near the roof, and screw the antenna on. Remember to make sure it’s pointing in the right direction (ie. towards the nearest mast).
You might also choose to mount your antenna on a pole to raise it higher than your house. If you’re going for this option, always make sure that it is stable and won’t cause any damage to the building you are mounting it to. It’s also worth liaising with your local authority before installing a large pole as in some areas, a tall pole could be in breach of planning rules.
You will also need to drill the cable into the house – It’s very important to avoid any other electrical cables and water pipes whilst you are doing this as well as sealing up the holes afterwards.
It’s also pretty important to keep the position of your router in mind. Will it be placed near the where the cable feeds into the building? Ideally, the cable between your antenna and router needs to be 5 metres or less otherwise you could find yourself struggling with interference and/ or signal loss.
If that all feels a little daunting then you can hire a professional installer to do the job for you – Our expert Wi-Fi engineers here at Geekabit can do just this! We operate out of Hampshire, London and Cardiff.
Whilst the physical aspects of installing an external antenna are quite straightforward, it’s not always easy to choose the right kit. The radio spectrum is variable by nature, which makes it very dependent on your environment. You might manage to install the antenna but not get the outcome you were expecting.
What antenna you need depends on your specific location and needs. This blog will outline some of the options that could be right for you. Sometimes it’s a case of trial and error to find the right antenna for you – But that’s where it might be best to leave it in expert hands.
‘Do I need an Omni-directional or Directional antenna?’
When it comes to installing an external antenna, the first thing you need to decide is whether you need an Omni-directional antenna or a Directional antenna.
Choosing a Directional antenna
If you know where your nearest mast is and have a clear line of sight, then the Directional antenna might be the one for you. Whilst it’s weaker in other directions, the Directional antenna will have higher reception in one direction, hence why it works well for a clear line of sight with the mast or base station. This is often the better choice if you live or work in a rural area.
What problems can you have with a Directional antenna?
Using a Directional antenna can run into issues if the station is congested or goes out of service. E.g. during upgrades.
Choosing an Omni-directional antenna
If you live or work in a more urban, built up area and aren’t sure where the nearest mast is then an Omni-directional antenna could be the better option for you. Whilst they have a lower overall gain, they are able to attract similar reception from all directions. Because the Omni is looking at a wider area, you may find that it provides better reliability.
Generally, if you are finding and installing an external antenna yourself, then the Omni-directional antenna is probably the one to try first.
What problems can you have with an Omni-directional antenna?
It’s possible that because it’s looking at a wider area, the Omni could attract more interference. If you are able to utilise a well positional Directional antenna then you could get better performance that way.
‘How much power does my external antenna need?’
So you’ve decided whether you need an Omni-directional or Directional antenna. What do you need to consider next?
You’ll notice that antennas have gain figures in dB / dBi – This is how the power of the antenna is measured.
In simple terms, the gain of an antenna is the relative measure of its ability to direct radio frequency energy in a certain direction or pattern. What do the gain (dB / dBi) figures on an antenna mean?
We could go into a lot of complicated detail here, but seeing as we’re writing this blog for someone looking to buy and install their own external antenna, we’ll keep it super simple.
Basically, the higher the gain (dB / dBi) the better the antenna’s performance and range. Obviously, the higher the gain, the more expensive the antenna will cost.
When you are at this stage of choosing your antenna, it is worth knowing what bands your mobile operator uses so that you can ensure how the different gain values given for an antenna correspond to the spectrum band you will be using.
‘Choosing an external antenna – What are the challenges?’
As we said above, when you are installing a new external antenna, it’s really important to know:
- Where and which direction the signal is coming from
- How strong the signal is
- Which bands are being used in your local area by local operators
These are some of the biggest challenges you’ll face when installing your antenna.
‘How can I find out the spectrum information I need to choose an antenna?’
If you go online to mobile operator’s websites you can find coverage checkers (Vodafone, Three UK, O2 and EE (BT)), but these can be rather vague and not always accurate. It’s worth comparing to what Ofcoms Mobile Coverage Checker says too.
Perhaps the best way to identify which bands are being used by your local operator is to download a relevant app or look up the mobile network details on your Smartphone or router.
These apps will often just tell you the band number for your own operator rather than tell you the spectrum frequency. You’ll find that operators tend to own several bands, but usually use one band for national connectivity.
What are the most common 4G Mobile Bands in the UK?
800MHz (Band 20)
900MHz (Band 8)
1800MHz (Band 3)
2100MHz (Band 1)
2300MHz (Band 40)
2600MHz (Band 7)
Remember that 5G uses a different band model and is currently only deployed on the 3.4GHz band.
‘How do I know where my nearest mast is for installing my new antenna?’
So you’ve made sense of the bands on offer in your area from local operators. Next you need to work out where your nearest mast is and whether it’s the most appropriate for your location. Unfortunately it’s not always the option that looks most logical!
When you’re choosing the most appropriate mast for your use, you need to consider the following:
- Forms and features of local land surfaces (artificial and natural)
- Local surroundings
- Operator choice
There are apps and websites that can help with this such as Mastdata.com and Cellmapper.net. The Opensignal app could also be of use.
Did you know that operators also have sharing agreements with each other? Just to make things a little more complicated. For example, there is a sharing agreement between Vodafone and O2 as well as between EE and Three. What does this mean? Well it means that a mast could be serving more than one operator.
How do I use signal strength information to position my external antenna?’
If you are able to gain an understanding of signal strength in a few different measurements, then you are more likely to position your antenna correctly.
Signal strength is measured in quite a few different ways, so we’re going to just focus on a few that you are most likely to encounter. These are:
- Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
- Reference Signals Received Power (RSRP)
- Reference Signal Received Quality (RSRQ)
These measurements are given by a negative dBm (decibel milliWatts) value. In this situation, negative values are actually good (most of the time). They are negative because they represent tiny yet positive numbers on a logarithmic scale, making them easier to consume. For example, -100dBm would be 0.0000000001 mW.
What is a good RSSI signal? Essentially, the closer to 0 dBm, the better the RSSI signal (although it does get more complicated past a certain point with diminishing returns of data speed). An example of excellent 4G RSSI signal would be -65 dBm. A poor RSSI signal would be -85 dBm.
RSRP works on a similar scale to RSSI, where an excellent 4G RSRP signal would be -80 dBm.
RSRQ operates on a very different scale, which means that an excellent signal is anything from around -10 dB (not dBm) and a poor signal would be -20 db.
Interestingly, most mobile modems are able to maintain a pretty fast data connection using a poor signal. Problems may arise however in more rural areas where speeds are slower and stability poorer due to the distance from a mast.
What factors are most likely to affect signal strength?
- Distance to mast
- Interference from competing signals
- Router band switching
- Physical obstacles in the environment like buildings, tall trees etc
- The weather
Of course, these factors are not in your control, but you need to bear them in mind when positioning your antenna in order to get the best signal possible.
Feeling confident about choosing and installing your external antenna?
If you are about to choose and install an external antenna to improve your 3G, 4G or 5G mobile broadband signal, then hopefully this blog has given you some of the basic information you need to make your decisions.
If you’re still feeling a bit daunted, then why not get in touch with one of our Wi-Fi experts? We’ve been installing mobile broadband for clients in and around Hampshire, Cardiff and London for a while and can help identify which antenna solution would best suit your needs. Get in touch today!