The WBA (Wireless Broadband Alliance) has recently released their latest Annual Industry Report (you can read it here). WBA CEO Tiago Rodrigues has subsequently revealed 10 predictions about how wireless technology will be used by communities and businesses across the globe in 2024 and beyond – From improved connectivity to new consumer experiences.
What will 2024 have in store for the world of Wi-Fi? Here are the 10 Wi-Fi predictions made by WBA CEO for next year and beyond
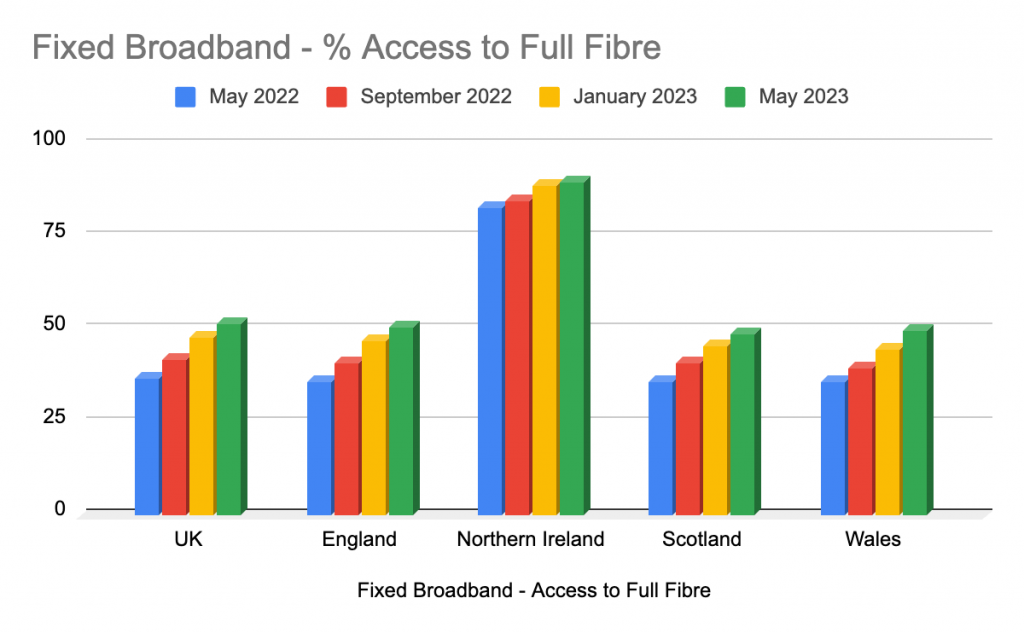
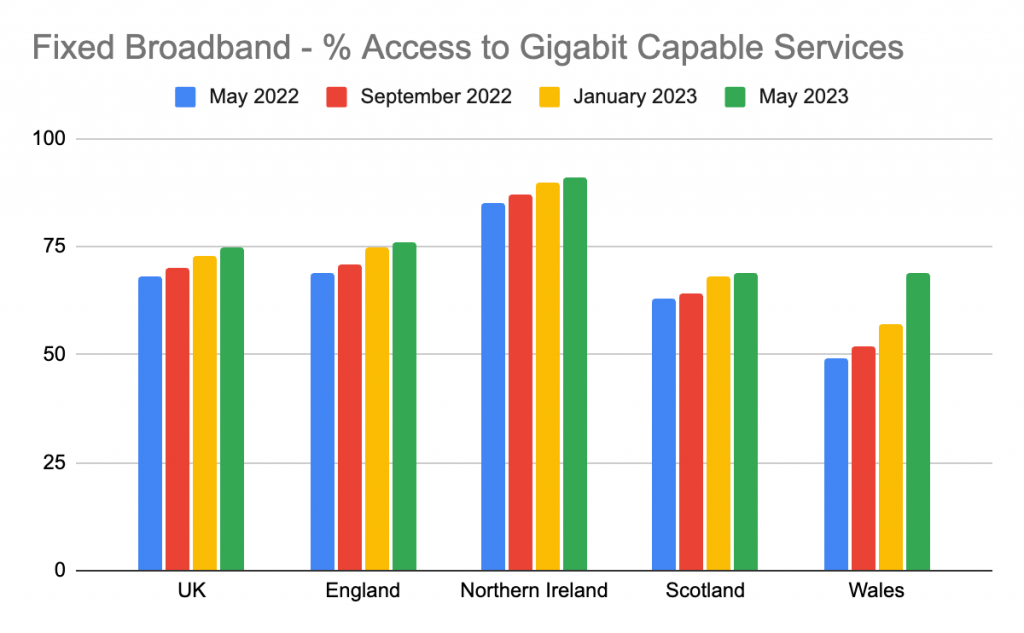
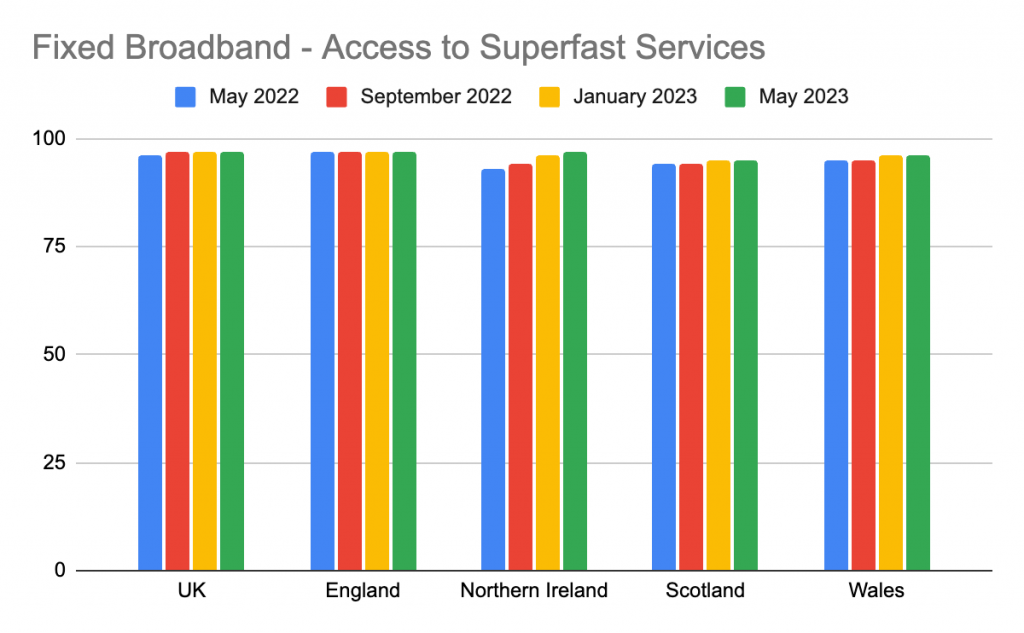
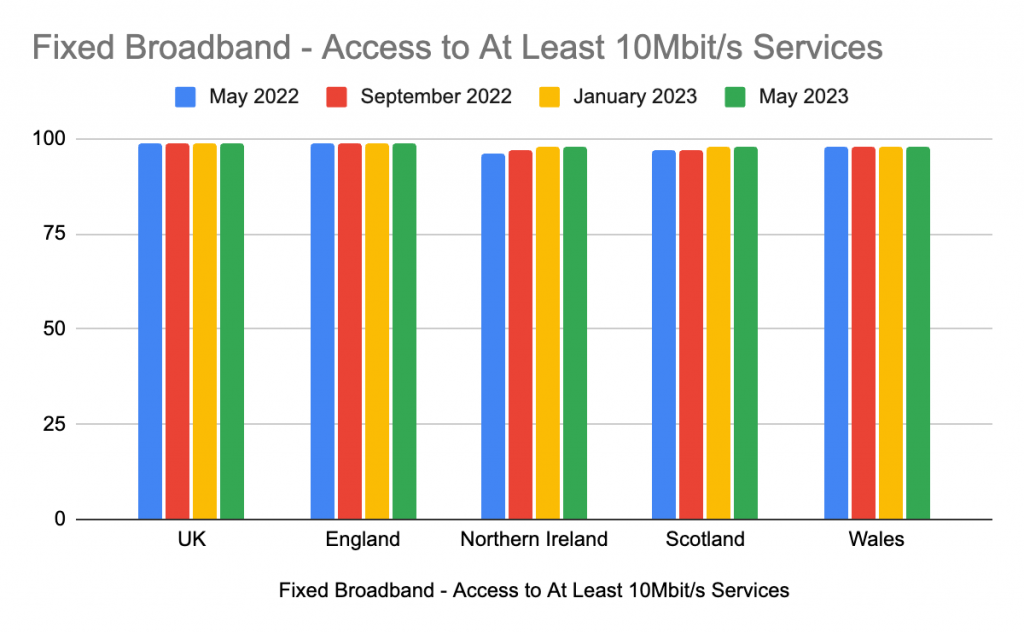
- Prevalence of Gbps, fibre broadband and Wi-Fi 6E/7 to increase
Moving forwards, speeds of 10 Gbps will become more prevalent. The deployment of fibre broadband will continue in most developed and developing markets. This will in turn create a need for home networks to make upgrades in order to utilise this increased bandwidth with their devices. The knock on effect of this will lead to a rapid adoption of Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7. The new ability to access additional spectrum in the 6GHz band will also drive the adoption of Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 as countries open the band. - Wi-Fi 7, gaming and video
With Wi-Fi 7 comes increased capabilities for advanced gaming, video content and immersive experiences. It’s forecasted that video game revenue globally could increased by 50% over the next 5 years. Network equipment will be as vital to gaming as the gaming rig itself. Wi-Fi 7 will be the driving force for the speeds needed as well as near-to-zero latency.New immersive experiences will see game developers breaking barriers. We’ve already started to see Wi-Fi 7 devices with Qualcomm chipsets this year and this will continue into 2024. - OpenRoaming, 5G and IoT networks
The growth of OpenRoaming is set to continue into next yet, extending further in order to integrate with private 5G and IoT networks. By 2026 it will have reached a critical point of exponential growth with the enabling of tens of millions of hotspots. PassPoint OpenRoaming deployments continue to rise, with more brands and identity providers recognising the value, enabling seamless connectivity across different networks. - Co-existence of 5G and Wi-Fi 6E / Wi-Fi 7
The integration of 5G services and Wi-Fi will progress, with the expectation that network engineers will deploy both Wi-Fi and cellular in the coming years. For example, using Wi-Fi 6E/7 for indoor, on-campus, fixed network situations and 5G in outdoor, off-campus, mobile environments. The Wi-Fi community is working to coexist with 5G, especially in identity management, authentication and policy management cases. - Network as a Service
NaaS is currently seen in managed Wi-Fi services in multi-apartment units and will continue to spread beyond these early adopters. Traditional enterprises will acquire NaaS for networks in cloud-first, software-defined, application-centric environments. Why is NaaS attracting customers? Because not only does it accelerate the deployment of devices but it also simplifies it. It also improves security with continuous security updates that prevent and reduce outages and breaches. - Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The role of AI and ML cannot be overemphasised. Adaptive AI is predicted to rapidly increase on networks. Not only will it enable Automated Frequency Coordination, it will also be able to predict network resourcing needs. We will also see AI help enterprises and Internet Service Providers accelerate troubleshooting and streamline monitoring as well as proactively anticipating outages, equipment failures, and performance degradation. - Outdoor Automated Frequency Coordination and Rural Connectivity
In countries that have opened large parts of the 6GHz spectrum to Wi-Fi, rural connectivity will find success with outdoor AFC. The rapid growth of 6GHz low-power indoor (LP) devices with an average transmit power of 24 dBm is expected for indoor applications such as residential mesh, indoor public venues, and high-density enterprise networks. The adoption of 6GHz very low-power indoor (VPI) devices with 14 dBm maximum transmit power is also expected for short-range indoor applications such as AR/VR/XR, streaming, and gaming. Users of these devices do not require Automated Frequency Coordination (AFC). - Unified connectivity with IoT tech and Matter
Smart home users will transform their experience with new IoT technology, helping to unify connectivity across multiple devices within the home. Matter will also provide a reliable, secure connection across multiple device manufacturers. The adoption of Matter certified products is expected to grow exponentially in the next 3 years, largely due to the brands involved in manufacturing the devices, like Apple, Amazon, Google and Samsung to name but a few. This adoption of Matter enabled devices in the Smart home will further validate Wi-Fi’s role as being central to the smart connected home. - TIP Open Wi-Fi to rapidly increase
Community-developed, disaggregated Wi-Fi software system TIP Open Wi-Fi will rapidly grow through further pilot projects and trials in developing countries and price-sensitive markets. This is due to its cost-effectiveness and the benefits offered by an open disaggregated model. The more well-established WLAN vendors will also continue to try and be more cost-effective in these markets by investing in ML and AI as well as offering integrated Wi-Fi and 5G to enterprises. - Prevalence of augmented and virtual reality will increase in homes and workplaces
Our day to day lives at home and work will start to see a larger share of augmented and virtual reality. This in turn will mean that indoor broadband networks will be required to adapt and improve in user interfaces and network capabilities, particularly when catering for larger groups of users. By 2025, it’s expected that the metaverse’s economy will generate $800 million (and $2.5 trillion by 2030). Thus, big brands are investing in this technology as the universe of the future.
What does Tiago Rodrigues have to say?
“There has never been a more exciting time for Wi-Fi with technologies such as OpenRoaming more widely available than ever and addressing the challenges in areas including Guest Wi-Fi provision, IoT deployments and private cellular networks. The HaLow program is creating huge interest in low-power extended range Wi-Fi and we are looking forward to working with the Wi-Fi ecosystem to develop industry trials for Wi-Fi 7 during 2024.”
CEO of the Wireless Broadband Alliance